Which Countries Still Have a Monarchy?
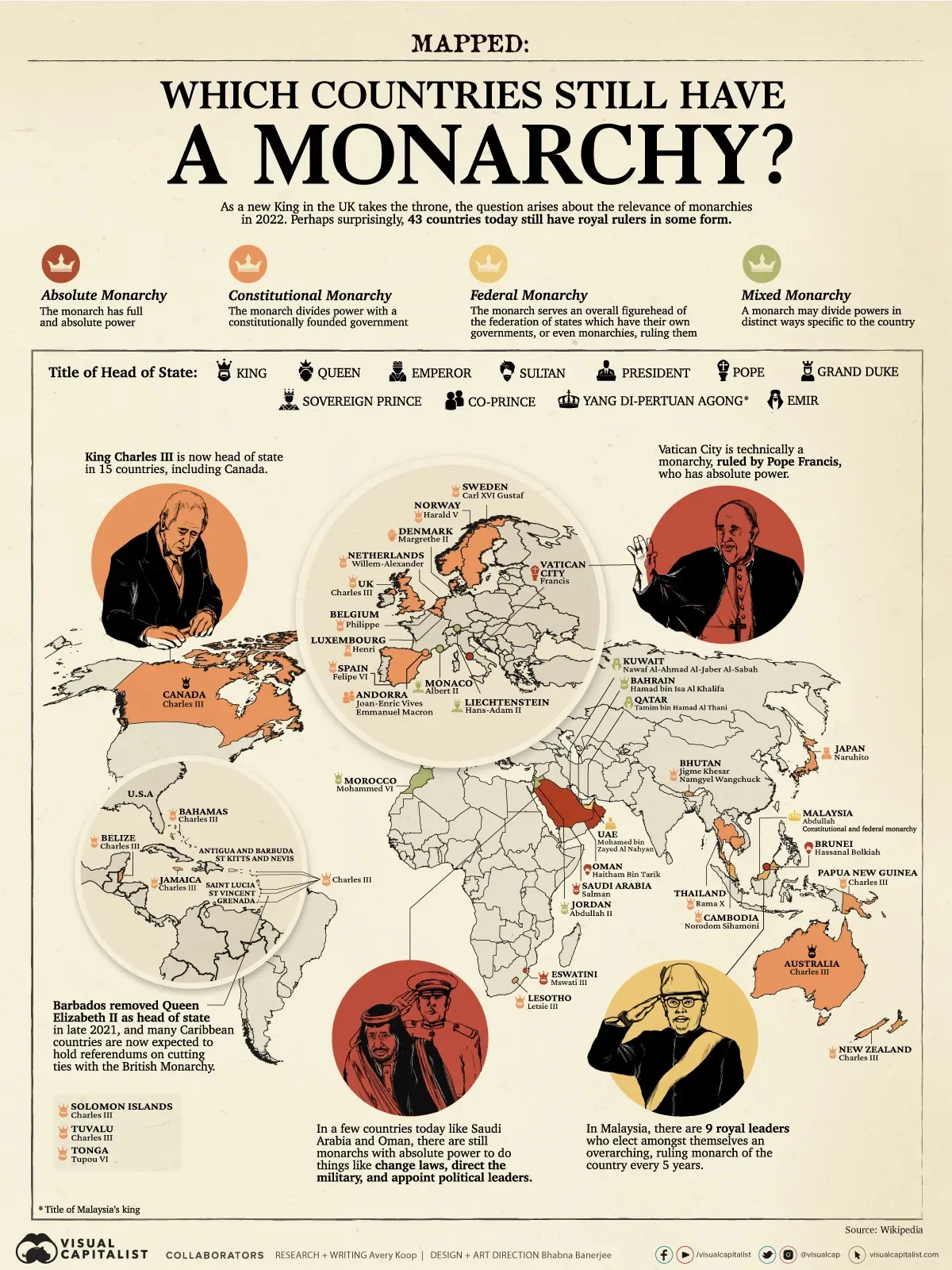
in this visual we break down the kinds of royal leadership across the 43 countries that still have them.
Types of Monarchies
A monarch in the simplest sense is a country’s king, queen, emir, or sultan, and so on. But before diving in, it’s important to break down the distinctions between the types of monarchies that exist today. Generally, there are four kinds:
① Constitutional Monarchy
The monarch divides power with a constitutionally founded government. In this situation, the monarch, while having ceremonial duties and certain responsibilities, does not have any political power. For example, the UK’s monarch must sign all laws to make them official, but has no power to change or reject new laws.
Here are some examples of countries with constitutional monarchies:
🇯🇵 Japan
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇩🇰 Denmark
② Absolute Monarchy
The monarch has full and absolute political power. They can amend, reject, or create laws, represent the country’s interests abroad, appoint political leaders, and so on.
Here are some examples of countries with absolute monarchies:
🇸🇿 Eswatini
🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia
🇻🇦 Vatican City
③ Federal Monarchy
The monarch serves an overall figurehead of the federation of states which have their own governments, or even monarchies, ruling them.
Here are some examples of countries with federal monarchies:
🇦🇪 UAE
🇲🇾 Malaysia
Malaysia is a unique form of federal monarchy. Every five years, each state’s royal leaders choose amongst themselves who will be the monarch, or the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, of Malaysia and the respective states. Furthermore, the monarchy is also constitutional, allowing a democratically elected body to govern.
④ Mixed Monarchy
This is a situation wherein an absolute monarch may divide powers in distinct ways specific to the country.
Here are some examples of countries with mixed monarchies:
🇯🇴 Jordan
🇱🇮 Liechtenstein
🇲🇦 Morocco
Interestingly, Liechtenstein is the only European monarchy that still practises strict agnatic primogeniture. Under agnatic primogeniture, the degree of kinship is determined by tracing descent from the nearest common ancestor through male ancestors.