Democracies tend to have lower levels of corruption
What difference does it make when people can choose their leaders? One area where the right to vote for political leaders may matter is corruption.
Democracy and corruption are hard to measure. One possible way to understand how countries perform on these fronts is to ask experts who study them closely. These expert judgments aren’t perfect, but we think they’re useful.
The V-Dem project surveys experts to assess how democratic each country is. Are elections free and fair? Do all citizens have equal voting rights? Are fundamental freedoms — like speech and assembly — respected? Experts also rate how frequent corruption is in public institutions, from bribery and embezzlement to whether laws are enforced fairly.
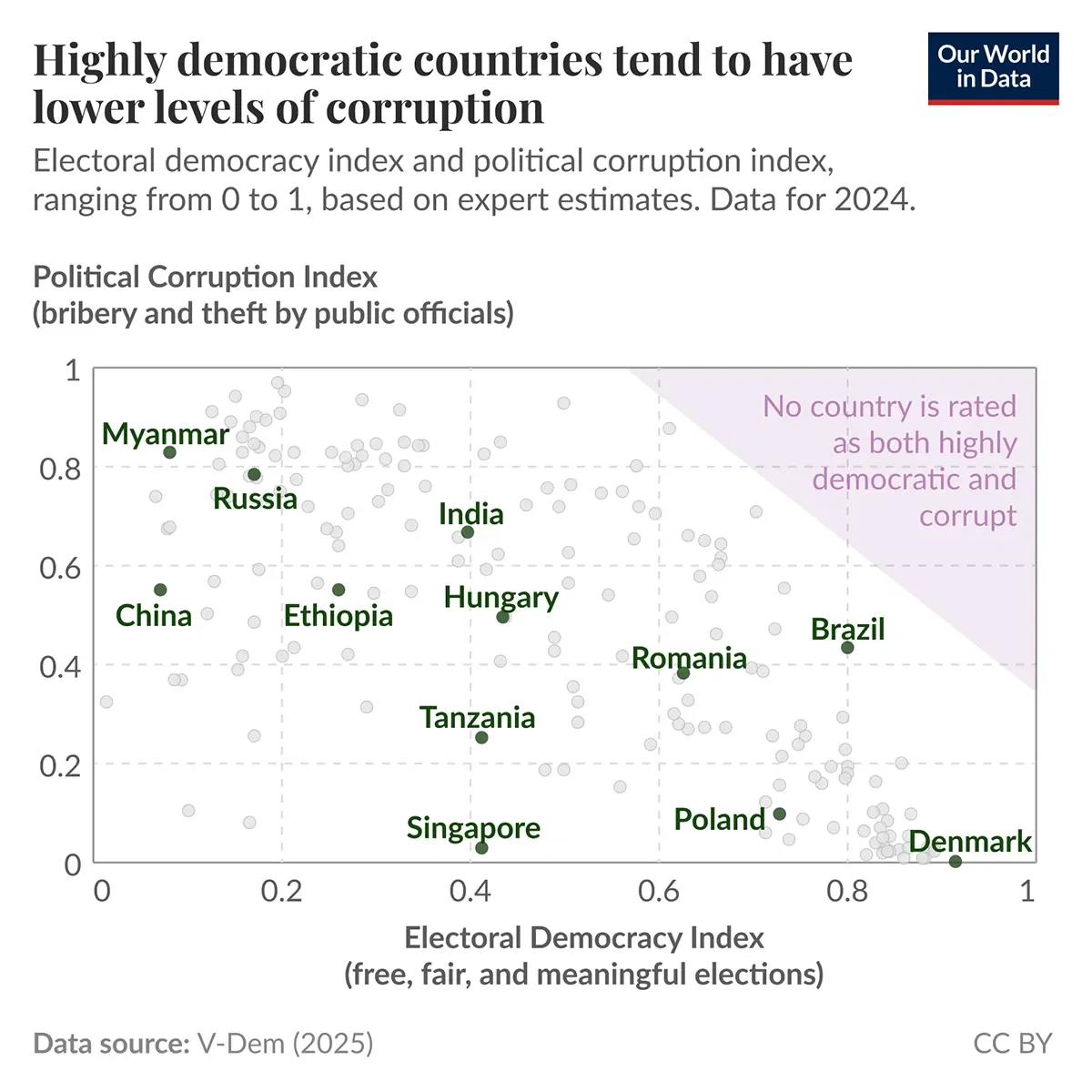
This chart combines these expert estimates: democracy on the horizontal axis and corruption on the vertical axis, with both scores on a scale from 0 to 1.
There are four corners in the chart. In the top left, you find many countries that are both autocratic and corrupt, such as Myanmar and Russia. In the bottom right, there’s a thick cluster of nations that have stronger democratic institutions and lower levels of corruption. What also stands out is that no country appears in the top right: none are rated as both having strong democratic institutions and being highly corrupt.
This chart shows correlation, not causation — but research on the causal link suggests democratic systems can indeed help expose and reduce corruption. And there is also a causal impact running the other way: corruption can weaken democratic institutions, for instance by lowering voter turnout.