Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2025. All rights reserved.
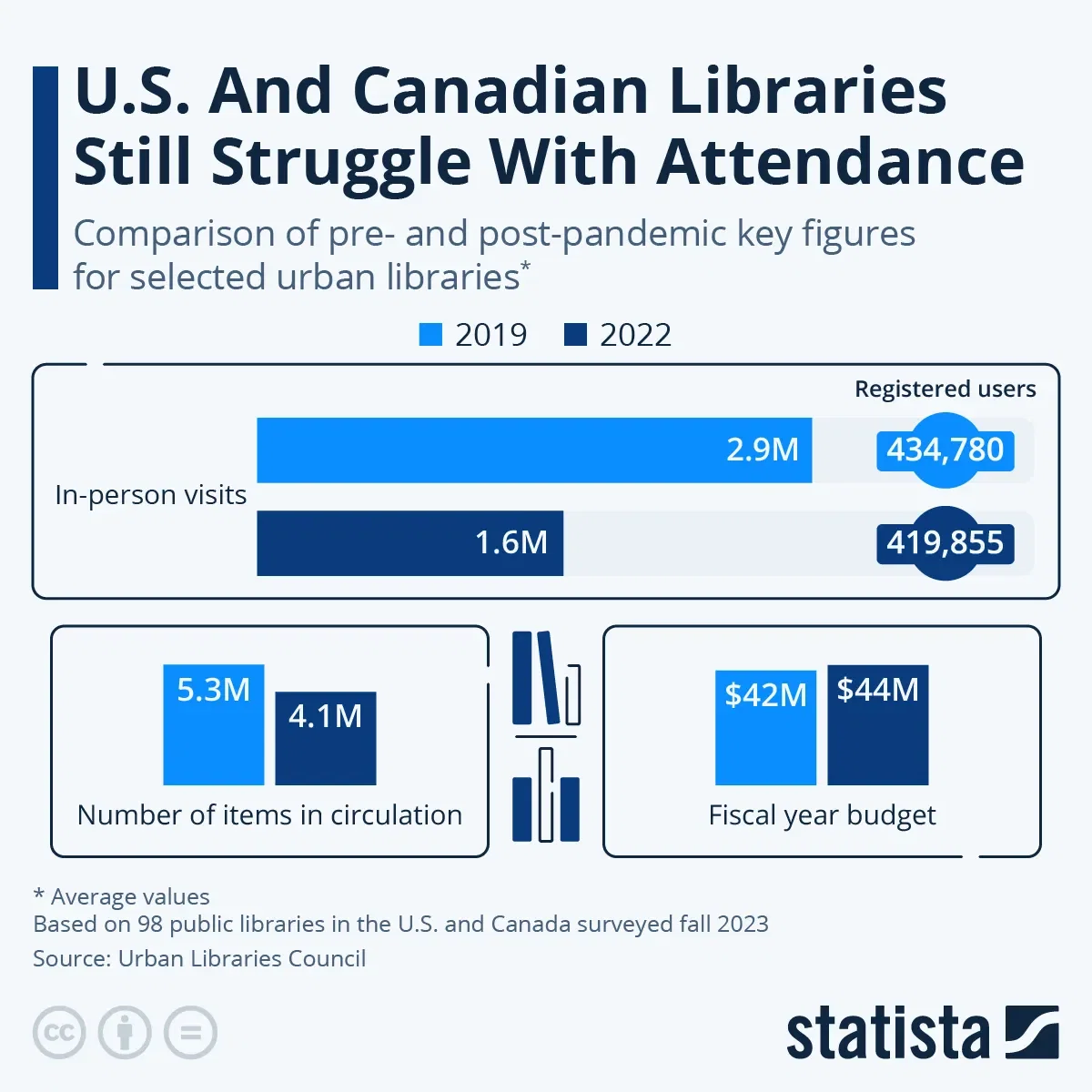
While there are many different types of libraries ranging from a school library to the Library of Congress, the form accessible to most U.S. residents is that of the public library. This library type is mostly financed by municipal taxes, state grants and donations by individuals and corporations. Even though libraries increasingly offer electronic resources, they are still seen as a physical gathering place and were drastically impacted by the coronavirus pandemic. A recent survey of 98 public libraries in Canada and the United States from the Urban Libraries Council shows that even though the budgeting for 2022 looked better than in the last pre-pandemic year, attendance and registered users didn't.
In 2022, the libraries surveyed recorded an average of 1.6 million visits, a decrease of 45 percent compared to 2019. The number of registered users decreased by roughly 15,000 individuals and circulated items dropped by 1.2 million to 4.1 million units. Nevertheless, the average available budget for the fiscal year 2022 increased by five percent.
While these budget numbers might seem astronomical for many smaller institutions, it's worth noting that many of the libraries surveyed are located in some of the biggest U.S. and Canadian cities like Toronto, Vancouver, Los Angeles, New York or Houston and therefore naturally have more funds at their disposal. For example, according to benchmarks from the Public Library Survey (PLS), 754 reporting public libraries from the state of New York exhibited total revenues of $1.5 billion in 2021, which marks the latest available comprehensive data, while Iowa's 534 public libraries had to make do with $142 million.
Overall, the PLS recorded 9,021 public libraries in the United States with revenues of roughly $15 billion, 86 percent of which came from the corresponding municipalities, seven percent from state coffers and only one percent from federal grants. Since 2018, the number of public libraries has remained relatively constant, while funding has steadily increased by about $1.2 billion between 2018 and 2021.