Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2026. All rights reserved.
The United States spends an unparalleled amount of money on its military—about $778 billion each year to be precise.
Additionally, the U.S. military also owns, leases, or operates an impressive real estate portfolio with buildings valued at $749 billion and a land area of 26.9 million acres, of which around 98% is located within the United States.
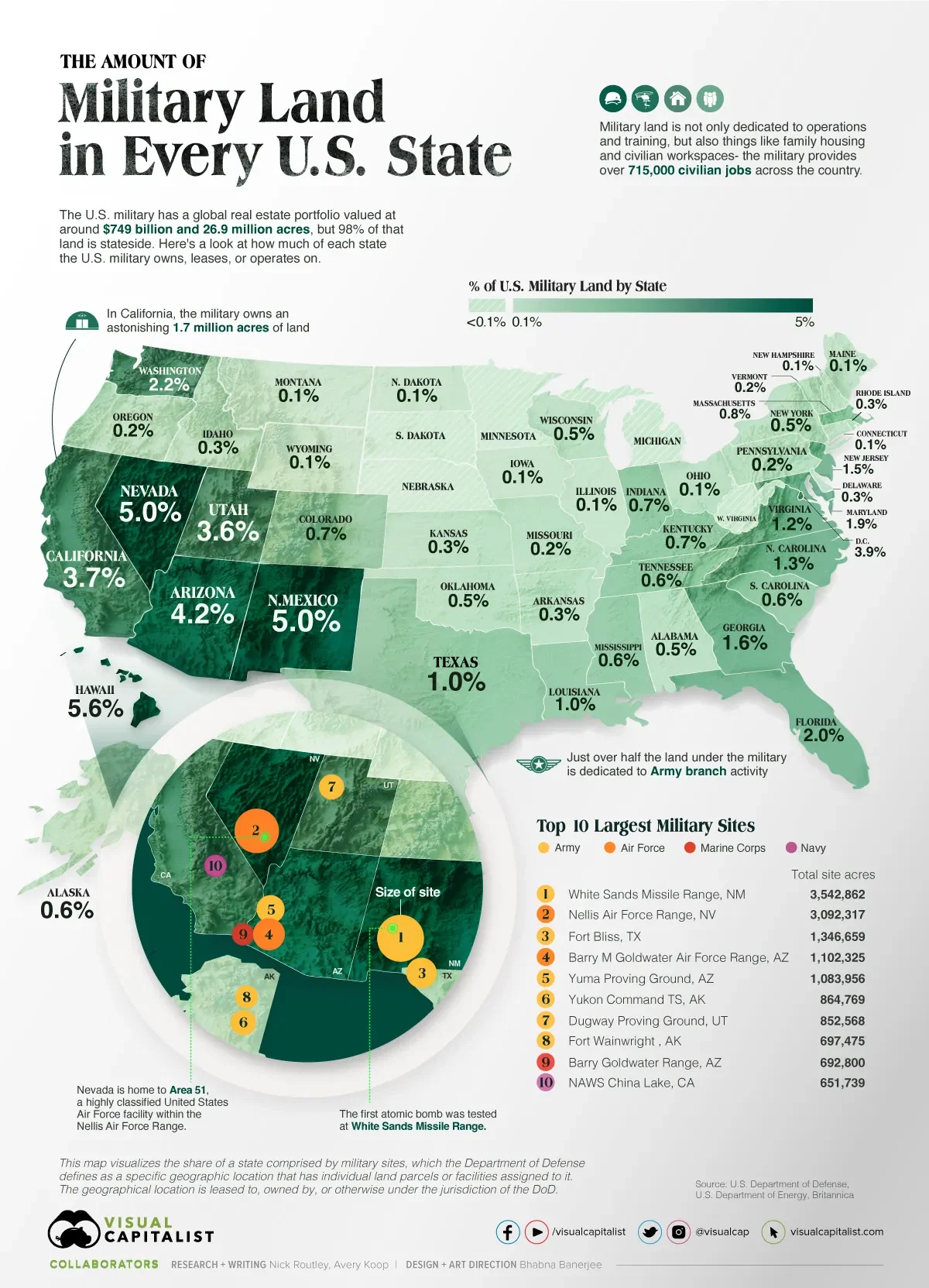
This visual reveals how much of each state the U.S. military owns, leases, or operates on.
What is Military Land Used For?
The DoD is the larger government umbrella under which the military falls and the department operates on over 26 million acres of land stateside.
To further break it down the U.S. military is divided into four main branches: Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps.
There is also the Space Force, the Coast Guard, and the National Guard. However, most of the land is dedicated to the Army, which is the military’s largest branch.
Military bases are used for training and housing soldiers, testing weapons and equipment, conducting research, and running active operations, among other things. A large majority of the square footage is actually designated for family housing.
For example, Fort Bragg, North Carolina, which is one of the most famous U.S. Army bases, is home to more than 260,000 people including the families of soldiers. The base, which is virtually its own city, is the largest U.S. Army installation with 53,700 troops—nearly 10% of the Army—and over 14,000 civilian employees.
Which States Have the Biggest Military Presence?
Looking at the largest total sites, the top 10 combined cover an astonishing 13,927,470 acres, larger than 10 individual states including New Jersey, Massachusetts, and Hawaii.
In Hawaii, 5.6% of the state belongs to the military. The historic Pearl Harbor on the island of Oahu is still an active base, housing both the Navy and the Air Force.
In the nation’s capital, Washington D.C., 3.9% of the small district is owned or operated on by the military—there are approximately 18 independent sites in the city.
Most of the DoD’s land is in the southwestern United States. One major benefit is that there are areas large enough in these states to test hugely destructive weapons without harming anyone. The atomic bomb was first detonated in the middle of nowhere in New Mexico at the White Sands Missile Range, the biggest military site in the country.