Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2026. All rights reserved.
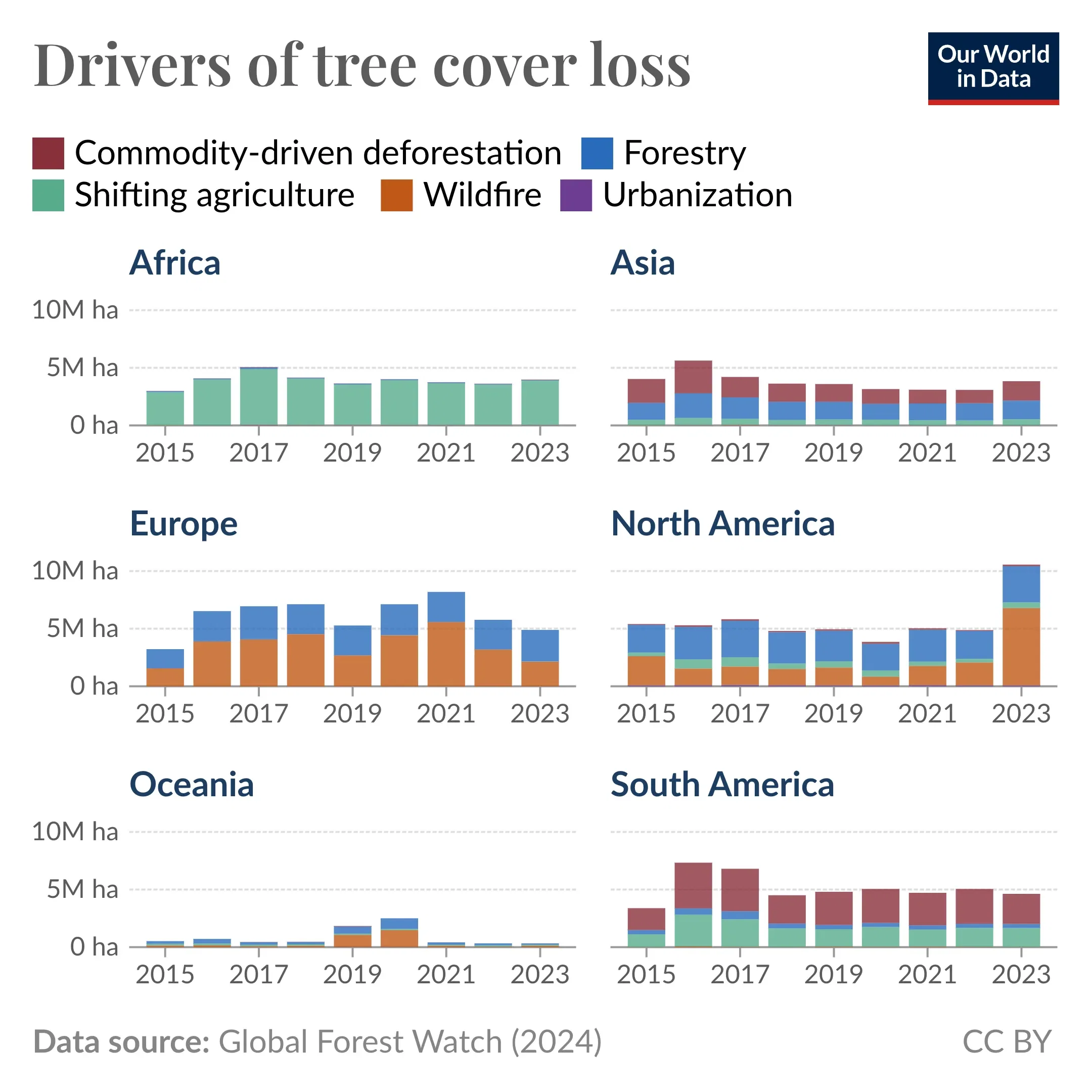
Recent data from Global Forest Watch shows trends in tree cover loss, split by five drivers: forestry, shifting agriculture, and wildfires, which lead to temporary tree cover loss, while commodity-driven deforestation and urbanization often cause permanent deforestation.
This dataset combines time-series data of tree cover loss, estimated from satellite imagery using research by Matthew Hansen and colleagues, with research on the drivers of deforestation by Philip Curtis and colleagues.
The drivers of tree cover loss vary markedly across regions. Wildfires and forestry (logging) are the main drivers of tree cover loss in Europe and North America, with wildfires mainly occurring in Canada and Russia. Tree cover loss from wildfires does not include fire clearing for agriculture.
Commodity-driven deforestation is a key cause in Asia and South America, largely due to trends in Brazil and Indonesia. Shifting agriculture — where trees are cleared so the land can be cultivated temporarily before being abandoned — is the dominant driver of tree cover loss in Africa and a major driver in South America.