Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2026. All rights reserved.
Global annual renewable capacity additions increased by almost 50% to nearly 510 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, the fastest growth rate in the past two decades. This is the 22nd year in a row that renewable capacity additions set a new record. While the increases in renewable capacity in Europe, the United States and Brazil hit all-time highs, China’s acceleration was extraordinary. In 2023, China commissioned as much solar PV as the entire world did in 2022, while its wind additions also grew by 66% year-on-year. Globally, solar PV alone accounted for three-quarters of renewable capacity additions worldwide.
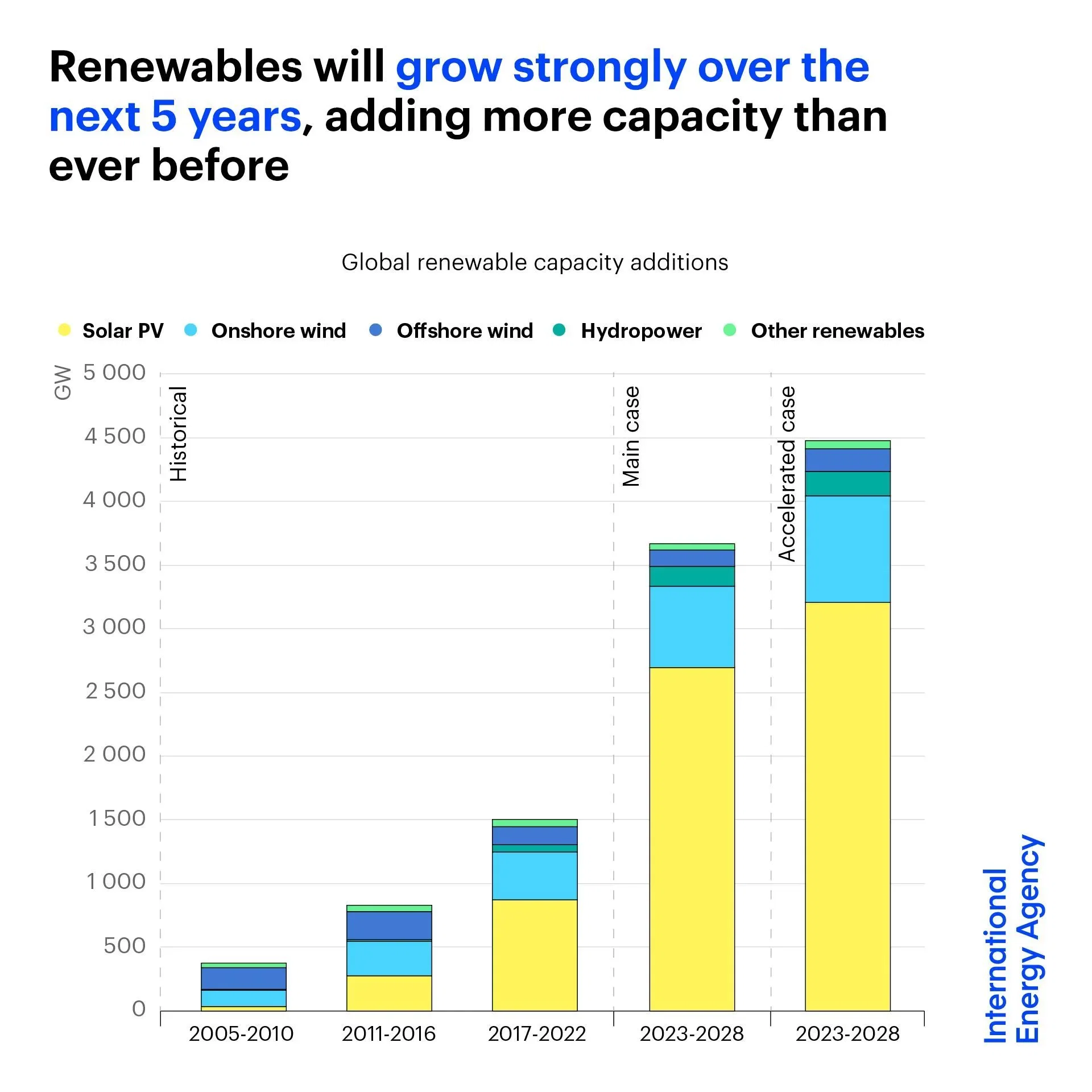
Prior to the COP28 climate change conference in Dubai, the International Energy Agency (IEA) urged governments to support five pillars for action by 2030, among them the goal of tripling global renewable power capacity. Several of the IEA priorities were reflected in the Global Stocktake text agreed by the 198 governments at COP28, including the goals of tripling renewables and doubling the annual rate of energy efficiency improvements every year to 2030. Tripling global renewable capacity in the power sector from 2022 levels by 2030 would take it above 11 000 GW, in line with IEA’s Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE) Scenario.
Under existing policies and market conditions, global renewable capacity is forecast to reach 7 300 GW by 2028. This growth trajectory would see global capacity increase to 2.5 times its current level by 2030, falling short of the tripling goal. Governments can close the gap to reach over 11 000 GW by 2030 by overcoming current challenges and implementing existing policies more quickly. These challenges fall into four main categories and differ by country: 1) policy uncertainties and delayed policy responses to the new macroeconomic environment; 2) insufficient investment in grid infrastructure preventing faster expansion of renewables; 3) cumbersome administrative barriers and permitting procedures and social acceptance issues; 4) insufficient financing in emerging and developing economies. This report’s accelerated case shows that addressing those challenges can lead to almost 21% higher growth of renewables, pushing the world towards being on track to meet the global tripling pledge.