Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2026. All rights reserved.
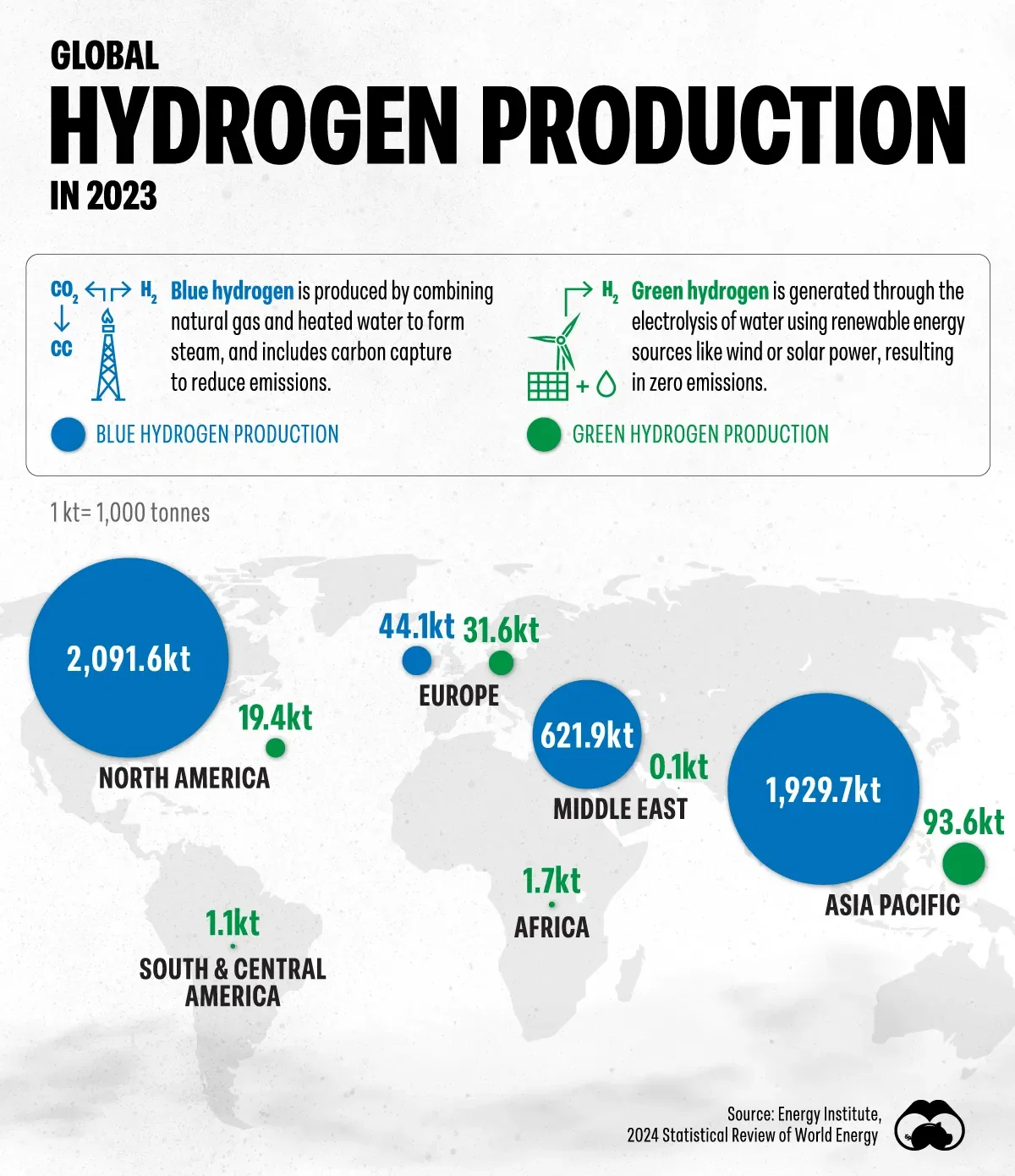
The total kilotonnes of hydrogen produced by each region in 2023, broken down by blue and green hydrogen.
Figures come from the Energy Institute's 2024 Statistical Review of World Energy and are updated as of June 2024.
Blue hydrogen production involves generating hydrogen from natural gas and steam, and using carbon capture to capture the resulting carbon emissions.
Green hydrogen production uses renewable energy to power electrolysis, a process that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in no carbon emissions.
Blue hydrogen production is currently much more prevalent than green hydrogen because it leverages existing natural gas infrastructure, making it easier and more cost-effective to produce compared to green hydrogen.
Green hydrogen is expensive primarily due to the high costs of renewable energy needed for electrolysis and the current inefficiencies in the technology.
Additionally, the electrolysis process itself is energy-intensive, contributing to overall costs.